Peaking/Bell filter
Syntax
Hd = peaking(Fo,BW,K,DFormat)
Description
Designs a 2nd order audio peaking/Bell filter. All frequencies are in Hz.
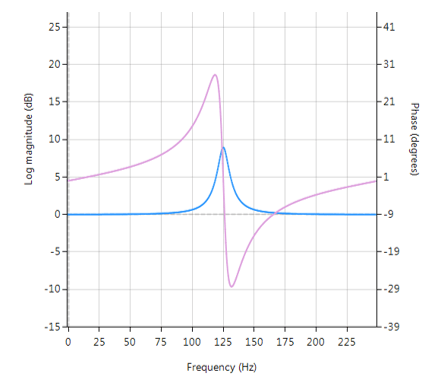
A Bell or Peaking filter is a type of audio equalisation filter that boosts or attenuates the magnitude of a specified set of frequencies around a centre frequency in order to perform magnitude equalisation. As seen in the plot below, the filter gets its name from the shape of the its magnitude spectrum (blue line) which resembles a Bell curve.
- K is amplitude of peak
- BW is bandwidth when K=0, and 0 < Fo < Fs/2
DFormat: allows you to specify the display format of resulting digital filter object.
symbolic |
Display a symbolic representation of the filter object. If the order > 10, the symbolic display option will be overridden and set to numeric |
numeric |
Display a matrix representation of the filter object |
void |
Create a filter object, but do not display output |
Example
[code lang=”java”]// Description: This script implements a simple 3-band audio equaliser
// Author: Advanced Solutions Nederland BV
// Date: Monday, 29 June 2020
//
// Tested with fs=44.1kHz
//
ClearH1; // clear primary filter from cascade
//band 1
interface f={10,1000,10,500}; // highpass filter
// band 2
interface BW = {1,2000,10,1500}; // filter bandwidth
interface fc = {0, fs/2,fs/100,fs/8}; // peak/notch centre frequency
interface K = {0,3,0.1,2}; // gain/sign
//band 3
interface BW2 = {1,2000,10,1500}; // filter bandwidth
interface fc2 = {0, fs/2,fs/100,fs/4}; // peak/notch centre frequency
interface K2 = {0,3,0.1,0.25}; // gain/sign
Main()
// design filters
hpfband={1,f};
Hdhpf=butter(2,hpfband,3,80,”highpass”,”symbolic”);
Hd1=peaking(fc,BW,K,”symbolic”);
Hd2=peaking(fc2,BW2,K2,”symbolic”);
// merge filters
Hd=augment(Hdhpf,Hd1,”void”);
Hd=augment(Hd,Hd2,”symbolic”);
// get coefficients
Num=getnum(Hd);
Den=getden(Hd);
Gain=getgain(Hd);
[/code]
See also
bessel / butter / cheby1 / cheby2 / ellip / arbmagphase / cplxfreqshift / dcremover / notch / peaking