There is an increasing use of the water infrastructure, while the current demand is already adjacent to the existing capacity. However, space for physical expansion is limited. On the other hand, there is a tightening of budgets, while maintenance of water infrastructure comes with high costs.
Huge cost savings as well as reducing public inconvenience can be achieved with a preventative maintenance program. Benefits of a preventive maintenance program are:
- A longer lifetime for your equipment with preventive maintenance
- Be in control and optimize your processes
- Optimize your just-in-time management and get more value by delivering guarantees
- Increase security for your cargo and your equipment
Struggle with the elements
Working at water is a struggle with the elements: water, wind, dust, heat, pressure. So, you want to know if pipelines are going to leak before they are actually leaking. When cables are beginning to wear out. If the oil is still on the right level. That you can act when dust or smear are blocking lenses. With IoT, you can predict and prevent equipment failure by monitoring product wear and replacement rates. As such, you improve the reliability of your assets and reduce downtime. And if you recognize little faults, you can solve them easily before they have become big and expensive problems.
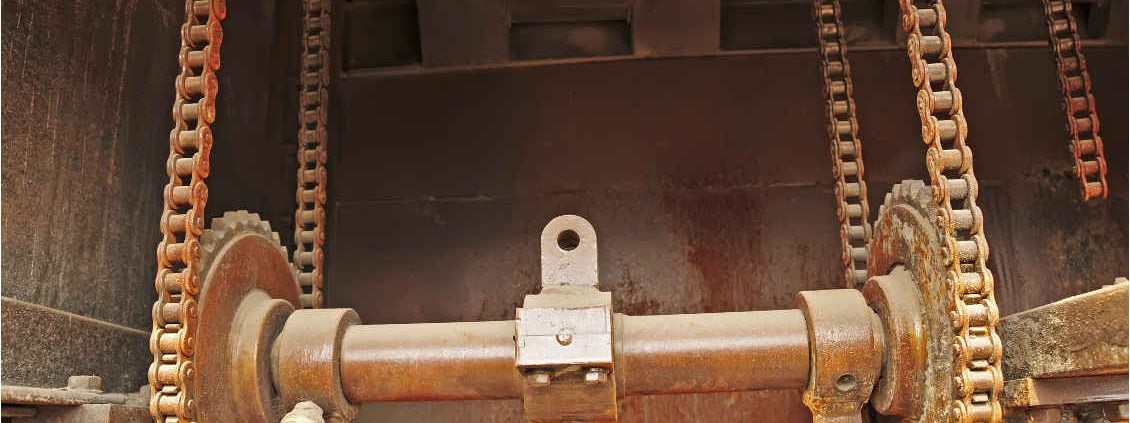
Rust
Another time- and money saver is the maintenance in the port: one of the worst enemies is rust. No wonder, that the in- and outside of the ship is painted very often. Even when there is no rust, ‘just in case’. It is better to place a rust sensor: it warns when there is rust and those places can be painted or otherwise maintained. And it makes sure spots are not forgotten. Even more: a rust sensor can track rust at places which are hardly reachable. An employee only has to go to this hard-to-reach part when it is really needed.
How preventive maintenance works
In essence, algorithms and analytics monitor sensor data. They look for deviations in a physical process’s normal operation. Examples are the wear and tear in a water sluice’s mechanical components, or even damaged wiring for the pump.
A sensor fusion algorithm merges data from different sensors. Associated analytics determine whether a component’s characteristic is normal for its age. Any deviations outside ‘normal operation’ are fed back to the master system as potential sources of failure.








Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!